In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the nursing care plan for DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis). But first, we need to know more about the DVT.
Thrombophlebitis is a serious condition of inflammation of the veins that results in blood clots or thrombosis that may hinder the normal flow of blood through vessels.
Venous thrombophlebitis occurs typically in lower extremities, or superficial veins like basilic, greater saphenous veins, and cephalic, that is usually not life-threatening.
This does not necessarily require hospitalization.
In the case of DVT or deep vein thrombosis, the blood clots may reach the bloodstream that may be life-threatening and lead to pulmonary embolism.
Once the blood clot travels through the bloodstream, it can obstruct the lungs and may block the normal blood flow.
The three contributing factors called the Virchow’s triad, results in developments of DVT that consist of hypercoagulability, injury of the vessel wall, and venous stasis.
Hypercoagulability occurs to patients with pregnancy, deficiency in fluid volume, blood dyscrasias, smoking, and the use of oral contraceptives.
Damage of venous walls may occur because of venepuncture, trauma, certain medications, and surgery.
Venous stasis occurs due to decreased blood flow such as in case of heart failure, medication therapies, and immobility.
The main goal of DVT treatment is to prevent the dislodgement of the blood clot.
This will reduce the risk of pulmonary embolism. The treatment of DVT also reduces the risk of any post-thrombotic syndrome.
If you rather learn how to do nursing care plan for DVT while watching a video, here is a quick thorough video for you.
If you rather learn while reading, just keep on reading.
See also: Can You Be a Nurse With Dyslexia?
Table of Contents
Nursing care plan for DVT in leg
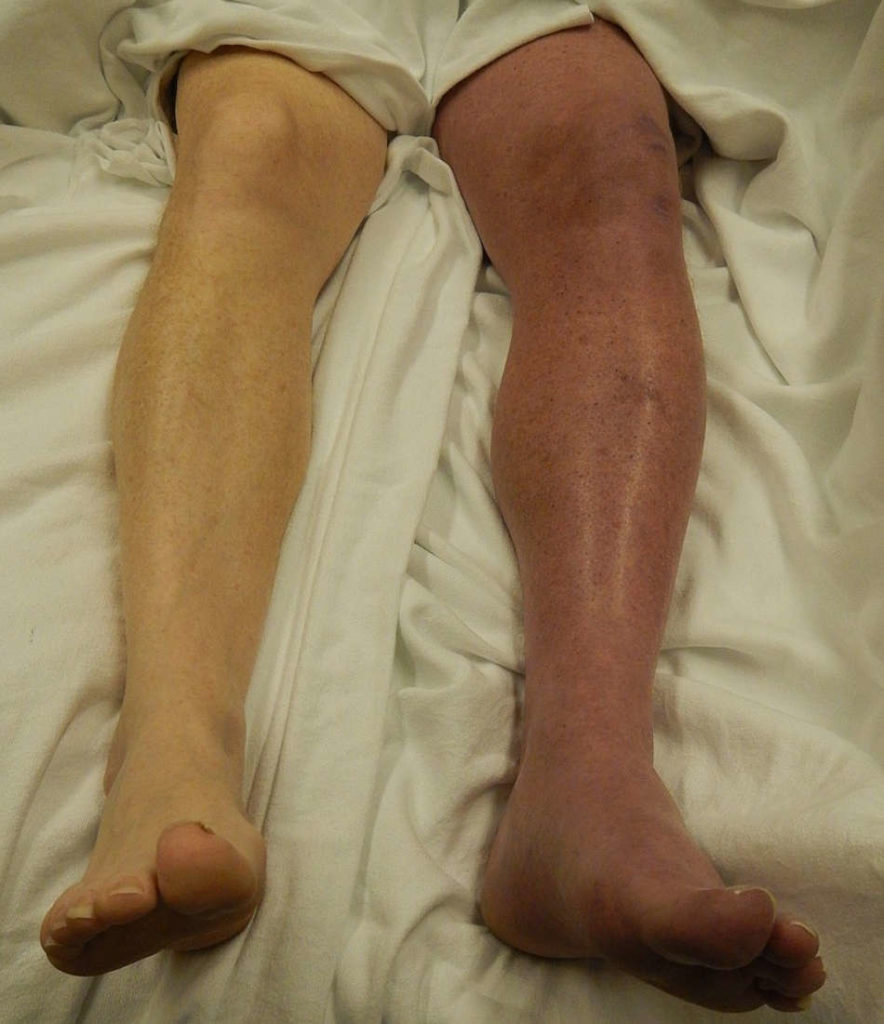
The nursing care plan for DVT in the leg may include:
- Information relating to the treatment, the disease condition and how to prevent it
- Monitoring and assessing anticoagulant therapy
- Offering comfort measures
- Providing information about the positioning of the body
- Encourage exercise
- Maintaining sufficient tissue perfusion
- Information relating to the prevention of complications
The following are five nursing care plans or NCPs for clients with DVT or Deep Vein Thrombosis:
- Impaired Gas Exchange – This involves the elimination of carbon dioxide on the alveolar-capillary membrane and deficit or excess oxygenation. The desirable outcomes of this nursing care plan involve the demonstration of adequate oxygenation and ventilation by ABGs that is within the normal range of the patient. The client displays or reports the absence or resolution of respiratory distress symptoms.
- Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion – This involves a reduction in oxygen that results in a malfunction at a capillary level to adequately nourish the tissues. The desirable outcomes include clients to maintain optimal tissue perfusion in the affected ends. This can be demonstrated by a reduction in or a reduction of pain, strong and steady palpable pulses, dry and warm extremities, and sufficient capillary refill. Typically, the clients do not even experience pulmonary embolism, as demonstrated by normal heart rate and breathing, absence of chest pain, and dyspnoea.
- Acute Pain – Acute pain causes unpleasant sensory and also emotional experiences that arise from potential or actual tissue injury or damage. Slow or sudden onset of intensity, be it mild or severe with the predictable end, in less than six months. The client will demonstrate controlled or alleviated discomfort or pain as a desirable outcome. He will show a relaxed manner, be able to rest or sleep or engage in a desirable activity. The patient will use verbal methods that will provide relief to him.
- Deficient Knowledge – Deficiency or absence of any cognitive information relating to any particular topic. The patient will express a clear understanding of the treatment, disease, and preventive measures.
- The risk for Bleeding – The risk for bleeding may decrease the volume of blood and compromise health. The desirable outcomes include maintenance of a therapeutic level of blood of anticoagulant which is demonstrated by PT or prothrombin time, INR or international normalized ratio, and PTT or partial thromboplastin time within a desirable range.
See also: Nursing Care Plan for Pneumonia – Full Guide
Nursing care plan for a patient at risk for DVT
A patient at risk for DVT refers to an extensive medical diagnosis that needs immediate medical intervention.
The nursing diagnoses put attention on symptoms and signs that require to be treated by a professional doctor.
See also: Can Nurse Practitioners Diagnose?
Medical interventions will be prescribed by the doctor for the medical nurse who will perform the nursing or medical interventions.
Even though the precise cause of DVT or deep vein thrombosis is vague and imprecise, the mechanisms that are more likely to be responsible for the development of DVT are:
- Damage – Any damage to the internal lining of the blood vessels develops a place for the blood to form clots.
- A reduced flow of blood – Reduced blood flow leads to venous stasis when the veins get dilated and the contraction of the skeletal muscles reduces.
- Platelet aggregates – Platelet aggregates are venous thrombi that are attached to vein walls with an appendage that looks like a tail and contains fibrin, many red blood cells, and white blood cells.
- Phlebitis – Thrombus formation normally accompanies phlebitis that is vein walls inflammations.
- Tail – The tail can propagate or grow in course of blood flow since thrombus forms in successive layers.
- Fragmentation – This can happen spontaneously when the thrombus naturally dissolves or when the venous pressure elevates.
- Recanalization – Reestablishment or recanalization of the vessel lumen, after an acute phase of DVT, typically occurs.
Sample nursing care plan for DVT
- Complete bed rest to avoid dislodgment of blood clots
- Elevate both or affected legs
- Avoid crossing legs while turning patient after every 2 hours
- Variety of motion exercises to the unaffected leg
- Reduce swelling by applying warm compresses
- Constant monitoring of the vital signs for every 4 to 6 hours
- Evaluate the performance of the patient for complexities of PE like chest pains, shortness of breath, cough, apprehension, hemoptysis, tachycardia, tachypnoea, fever, crackles, and diaphoresis.
Conclusion: Nursing care plan for DVT
You can prevent the development of DVT at home. If it is possible, exercise regularly, walking, bicycling, or swimming can help a great deal to manage your weight.
You should avoid smoking and keep an eye on your blood pressure.
Visit a doctor if you are facing any blood clotting issues or if you are pregnant or on contraceptive pills.
See also: Does Birth Control Pills Make You Gain Weight?
You must, at all times, drink lots of fluid, except alcohol and coffee.
This will help you to keep yourself hydrated and makes your blood thinner and veins broader. Avoid wearing tight clothes and do not cross your legs while sitting.
This will hinder the normal blood flow and leading to swelling.
At this point, you should know a lot about the nursing care plan for DVT. If you would like learn some more, check out these articles of ours:
- Nursing Care Plan – Full Guide & Free Templates
- Nursing Care Plan Hypertension – Full Guide
- Nursing Care Plan for Hypothyroidism
- Nursing Care Plan for Anxiety – Full Guide
- Nursing Care Plan for Depression
- Nursing Care Plan for Infection
I’d be glad if you could give this article a star rating. Thank you in advance!
